Pontic in Dentistry
The bridge is a part of the fixed bridge, and its design, classifications and configuration are very diverse.
Here we will collect and summarize the types and designs of bridges based on the personal efforts of a group of undergraduate students.
A bridge replaces a missing tooth with artificial (false) teeth that are usually attached to the dental prosthesis.
When a patient’s original teeth are lost as a result of dental trauma, root resorption, extensive periodontal disease, or unsuccessful endodontic treatment, the dentist will recommend placing a bridge in their place.
A “pontine” is an artificial tooth attached to a dental bridge in dentistry.
The bridge is constructed as a single prosthesis and looks like a natural tooth protruding through the gum because it relies on an abutment for stability.
The bridge is made entirely of ceramic or porcelain in this dental procedure code.
The appearance of a bridge made of either of these materials is desirable, as porcelain produces a more natural appearance than the “heavier” look of full ceramic.
This is why a wholly ceramic pontic is often used in the back of the mouth while an all porcelain one is typically used to heal decay on teeth in the “smile-zone.”
A pontic made of porcelain fused to a high noble metal would be a good substitute for this kind of pontic since it offers outstanding cosmetic advantages in addition to the durability that comes from the underlying metals.
A pontic of this kind would be made up of at least 60% of the noble metals gold, platinum, palladium, and silver.
The American Dental Association would award this honor if at least 40% of that 60% were gold.
Pontic classification
1_Based on the design of the surface-contacting ridge (Tylmann)
▪Sanitary
▪ Modified sanitary
▪ Spheroidal
▪ The saddle
▪ Ridge Lap
▪ Modified Ridge Lap
▪ Ovate
2_Rosenstiel claims that depending on mucosal contact
A. Ridge-to-mucosal contact
▪ Modified ridge lap
▪ Ovate
▪ The conical
B. No Mucosal Contact
▪ In a sanitary (hygienic)
▪ Modified sanitary
3. Based on the anatomical type (Johnston)
▪ sanitary
▪ hygienic form
4. Prefabricated Pontics
▪ Flat back
▪ Longpinfacing
▪ Trupontic
▪ Reversal pin facing
▪ Pontips
5_Based on materials used
▪ Metal
▪ Metal and porcelain
▪ Metal and Resin
Pontics with mucosal contact are classified as either ridge lap or saddle pontics.
These kinds straddle buccal and ridge’s lingual surfaces, which making a significant concave contact with is the ridge.
only employed in instances involving high standards for beauty.
Buccal and lingual forms provide benefits.
pontic replicate the nearby natural tooth, adding aesthetic value, A drawback is the pontic coating, Gum surface makes it challenging to maintain and clean.
Pontic does not make contact with the lingual portion of the ridge in a modified ridge lap
but does make contact with the ridge labially.

Areas with strong aesthetic visibility are an indication.
Advantage:
aesthetically pleasing and helps the patient keep the area tidy,
they do not come into contact with the tongue mucosa,
Cons: They don’t make cleaning as simple or sanitary pontic.
The most attractive design is the ovate pontic.
This suggests that the ponticc oming out of the ridge.
Signal: in areas of fresh extraction, Option for the anterior replacement teeth with high esthetic requirements
Benefits: natural outcome and mimicking a nearby real tooth,
accessible while brushing teeth.
disadvantages: limited to placement in the event that the ridge is concave.
Take extra precautions to prevent tissue inflammation.
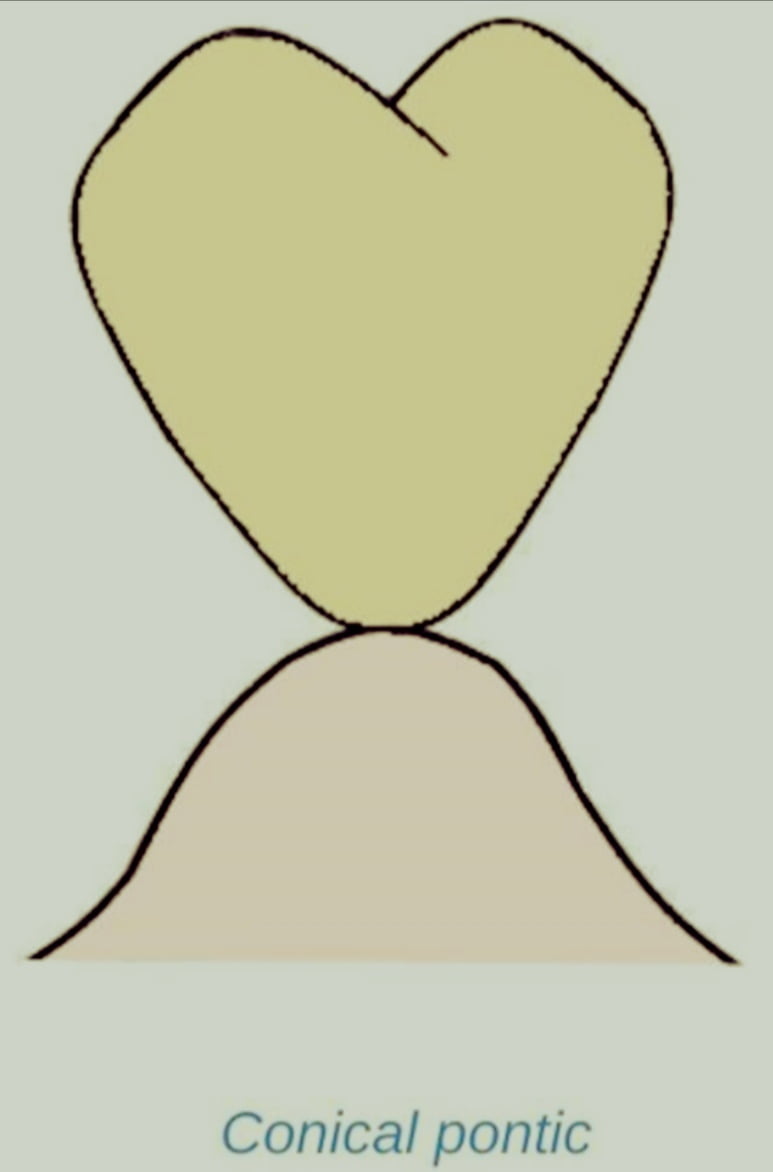
Conical Pontic:
A pontic structure contact with the ridge in one place
Message: molars that don’t call for aesthetic consideration.
Benefits: Good oral hygiene
maintained with ease clean
disadvantageous
poor esthetic
Pontics with no touch to the mucosa
No touching the residual ridge is allowed in a sanitary or hygienic pontic.
A non-esthetic zone is indicated.
without any prospect of finding food lodgement.
Advantage: Easy oral access
cleanliness,
limited tissue
inflammation.
disadvantageous
esthetics esthetic
Modified hygienic pontic and Perel
a lack of mesiodistal concavity, and faciolingually in the convexity undersurface.
A non-esthetic zone and in locations where food is unlikely lodgement.
Advantage: Easy oral access
minimal tissue inflammation, cleanliness.
Unacceptably bad aesthetics.
Options for pontic design:
The majority of researchers who studied pontic design believed that the buildup of plaque on the basal Surface of the aqveslar mucosa beneath pontics causes irritation.
a pontic. As a result, it was thought that glazed ceramics, with their low rate of plaque buildup, were the preferred material for pontics.
91% of the anterior regions of patients who were partly dentate were edentulous in a retrospective examination of the Jaw showed varying degrees of alveolar abnormalities.
A classification that works for Scibect offered information on alveolar ridge defects.
In a poll of patients with FPDS in the maxillary anterior region, 20% of respondents expressed dissatisfaction with the aesthetics of their denture, and 40% voiced concerns about food particles becoming trapped in the appliance . On patients with horizontal malformations in the wild (class I)
greater subjective satisfaction with their repair than did these patients whose restorations
Every flaw had a vertical element to it (classes II and III)
Conical Pontic: Rich Enhech’s research found that the conical pontic might be utilized to stop the preventing the extraction site from collapsing following tooth removal and limiting the normal
The tooth’s emergence . Because the nearby soft object has been in use for a long time
The tissues tend to swell until the alveolar bone is also resorbed. According to the evidence now available, these reactions most likely occurred because the bridge prevented proper dental hygiene.
A modified application of this technique, the immediate pontine method, to preserve the shape of the alveolar ridge after tooth extraction.