Maxillary nerve( V2 )
It is the second branch of the trigeminal ( 5th cranial ) nerve .
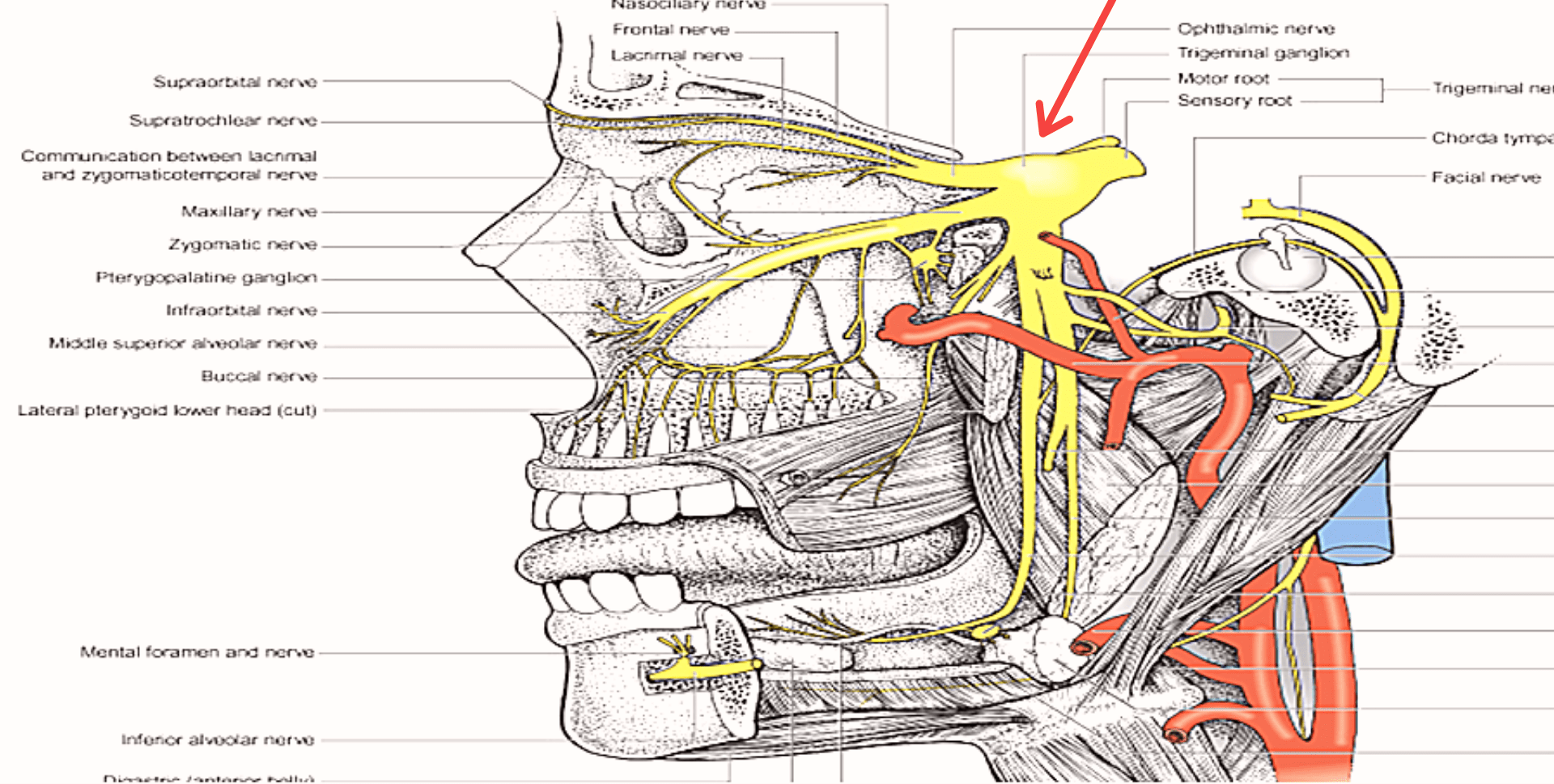
It exits the cranium via foramen rotundum of the greater wing of the sphenoid bone then travels at the superior most aspect of the pterygopalatine fossa just posterior to the maxilla giving branches according to its location i.e. inter-cranial , pterygopalatine , infraorbital , and facial.
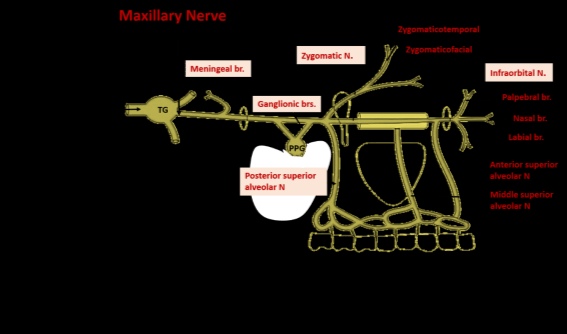
Branches
1. within the cranium
Middle meningeal nerve
providing sensory innervation to the dura mater
2. within the pterygopalatine fossa :
It gives off 3 branches ; zygomatic , pterygopalatine and posterior superior alveolar nerves
Zygomatic nerve :
- Zygomaticofacial nerve- skin of cheek prominence
- Zygomaticotemporal nerve- skin of lateral forehead
pterygopalatine nerves : or S.P.N :
It serves as communication for the pterygopalatine ganglion and the maxillary nerve .
It carries postganglionic secretory – motor fibers through the zygomatic branch to the lacrimal gland –
Pterygopalatine nerve branches
1. Orbital branches
supplies periosteum of the orbits
2. Nasal branches
supplies mucous membranes of superior and middle conchac , lining of posterior ethmoid sinuses , and posterior nasal septum.
Nasopalatine nerve
travels across the roof of nasal cavity giving branches off to the anterior nasal septum and floor of nose .
Enters incisive foramen and provides palatal gingival innervation to the premaxilla.
3. Palatine branches
greater and lesser palatine nerves
- Greater palatine : travels through the pterygopalatine canal and enters the palate via the greater palatine foramen .
It innervates the palatal tissue from premolars to soft palate .
Lies 1cm medial from 2nd molar region - Lesser palatine : emerges from lesser palatine foramen and innervates the mucous membranes of the soft palate and parts of the tonsillar region
4. Pharyngeal branch
exits the pterygopalatine ganglion and travels through the pharyngeal canal .
Innervates mucosa of the portions of the nasal pharynx.
Posterior superior alveolar nerve :
Branches from maxillary nerve prior to entrance into infraorbital groove .
Innervates posterior maxillary alveolus , periodontal ligament , buccal gingiva , and pulpal tissue ( only for 1st , 2nd , and 3rd molars )
3. branches within infraorbital canal
– Middle superior alveolar nerve
Provides innervations to the maxillary alveolus , buccal gingiva , periodontal ligament , and pulpal tissue for the premolars only
– Anterior superior alveolar nerve
Provides innervations to the maxillary alveolus , buccal gingiva , periodontal ligament , and pulpal tissue for the canines , lateral and central incisors
4_facial branches
Emerges from the infraorbital foramen as : a –
- Inferior palpebral- lower eyelid
- External ( lateral ) nasal – lateral skin of nose
- Superior labial branch- upper lip skin and mucosa.