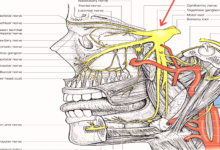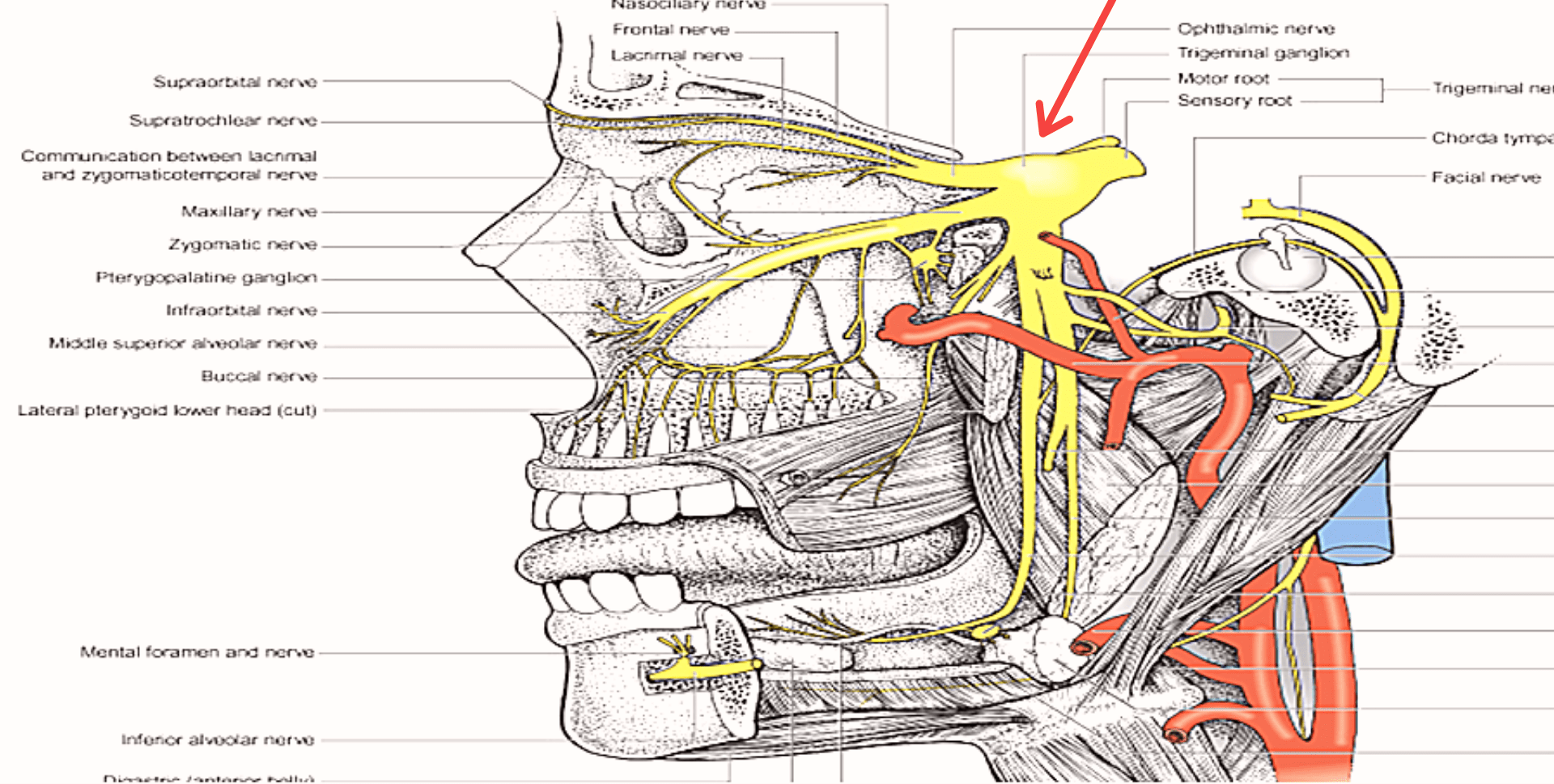
Anatomy and course of Mandibular nerve ( V3 )
It is the third branch of the trigeminal ( 5 cranial ) nerve .
It exits the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale .
It is the largest branch of the trigeminal nerve which composed of sensory and motor roots .
The sensory root originates at inferior border of trigeminal ganglion while the motor root arises in motor cells located in the pons and medulla and lies medial to the sensory root .
Branches The sensory and motor roots emerge from the foramen ovale of the greater wing of the sphenoid .
Branches of mandibular nerve
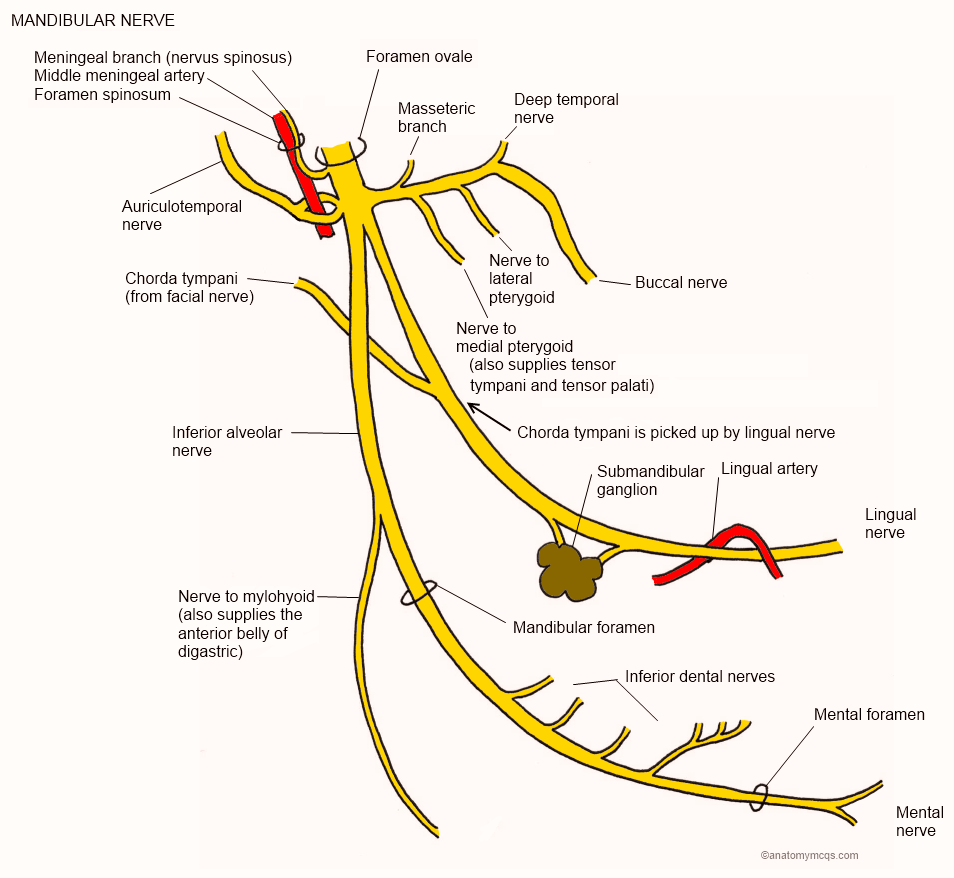
Initially merge outside of the skull and divide about 2-3mm inferiorly into :
Branches of the undivided nerve
Branches of the anterior division
Branches of the posterior division
Branches of the undivided nerve
- Nervus spinosus- innervates mastoids and dura.
- Medial pterygoid- innervates medial pterygoid muscle and gives off small motor branches to the tensor velipalatini and the tensor tympani .
Branches of the anterior division
three motor and one sensory.
Buccal nerve ( long buccal and buccinator )
supply buccal mucosa of 6-7-8 teeth,
It travels anteriorly and laterals to the lateral pterygoid muscle and from mucose to skin, gives branches to the temporalis, masseter and lateral pterygoid muscles.
It continues to travel in antero – lateral direction , at the level of the mandibular 3rd molar , branches exit through the buccinator and provide innervation to the skin of the cheek .
Branches also stay within the retromandibular triangle providing sensory innervation to the buccal gingiva of the mandibular molars and buccal vestibule.
temporalis.
masseter.
lateral pterygoid muscles.
Branches of the posterior division
Travels inferior and medial to the lateral pterygoid where it divides into :
Auriculotemporal
Lingual
Inferior alveolar and mylohyoid
Auriculotemporal :
Transverses the upper part of the parotid gland and posterior portion of the zygomatic arch giving off branches including the following :
- Communicates with facial nerve to provide sensory innervation to the skin over the zygomatic , buccal , and mandibular areas .
- Communicates with the otic ganglion to provide sensory , secretory and vasomotor fibers to the parotid .
- Anterior auricular- skin over helix and tragus.
- External auditory meatus- skin over meatus and tympanic membrane.
- Articular- posterior TMJ.
- Superficial temporal- skin over temporal region.
Lingual
It lies between ramus and medial pterygoid within the pterygomandibular raphe .
It lies inferior and medial to the mandibular 3rdmolar alveolus .
It provides sensation to anterior 2/3rds of tongue , lingual gingiva , floor of mouth mucosa , and gustation ( chorda tympani ) .
It is the nerve that supplies fibers for generalsensation , whereas the chorda tympani ( a branch of the facial nerve ) supplies fibers for taste .
Inferior alveolar nerve
It descends medial to the lateral pterygoid muscle to the region between the sphenomandibular ligament and the medial surface of the mandibular ramus and lateroposterior to the lingual nerve , where it enters the mandibular canal at the level of the mandibular foramen .
It provides innervation to the mandibular alveolus , buccal gingiva from premolar teeth anteriorly , and the pulpal tissue of all mandibular teeth .
Terminal branches of inferior alveolar nerve :
Incisive nerve
remains within inferior alveolar canal from mental foramen to midline .
Supply Periapalpal of 4.3.2-1 teeth.
Mental nerve
exits mental foramen and divides into 3 branches to innervate the skin of the chin , lower lip and labial mucosa.
Mylohyoid nerve
It is a mixed ( motor and sensory ) branch from the inferior alveolar nerve prior to entry into lingula .
It is motor to the mylohyoid muscle and the anterior belly of the digastric .
It also may provide sensory innervations to the mandibular incisors and pulpal innervations to portions of the mandibular molars in some persons , usually the mesial root of the mandibular first molar.